Strategic solutions for Life Sciences to mitigate challenges from parallel trade
What if your carefully curated pricing strategy, tailored to regional economic conditions and market demands, was washed away by someone else profiting from the difference?
This is the reality of parallel trade in the life sciences industry. This is where pharmaceuticals flow like an unstoppable current through unexpected channels, creating a shadow market that undermines carefully structured pricing models, revenues and threatens supply chain integrity. With significant implications for pricing, revenue and brand reputation, companies must strategize effectively to mitigate its impact.
The cross-border current
Parallel trade emerges when pharmaceuticals or medical devices are legally purchased in one country and resold in another without manufacturer authorization. While most prevalent in the European Union, where varying pricing structures and regulatory frameworks between member states create profit opportunities, this practice extends globally.
Australia and Canada maintain tightly regulated parallel trade systems to protect local supply, while regions like Asia and Latin America see smaller-scale activity, often in less regulated markets. Even the United States has explored Canadian drug imports as a potential solution to rising healthcare costs.
The ripple effects of parallel trade
Parallel trade exploits international price differences driven by varying economic conditions and regulatory environments. Though legal, it poses significant challenges for manufacturers and distributors:
- Revenue Erosion
When products meant for lower-priced markets are diverted to higher-priced regions, manufacturers face direct profit losses as their carefully structured pricing models collapse.
- Market Disruption
Price differentials designed to ensure global market access become unstable, undermining manufacturers' ability to maintain equitable pricing across different economic zones.
- Supply Chain Volatility
Product diversion from lower-priced markets creates unpredictable shortages, forcing manufacturers to manage complex supply imbalances across regions.
- Reputation and Quality Assurance Risks
By circumventing authorized distribution channels, parallel trade increases exposure to counterfeits and compromised handling, potentially damaging brand trust and patient safety.
- Regulatory Burden
You must navigate a complex web of national regulations, investing substantial resources in compliance monitoring and enforcement strategies.
Stemming the flow: Strategic solutions that work
Manufacturers and distributors must combat parallel trade through innovative technological and analytical approaches. While supply chain control and regulatory lobbying remain important, two key strategies emerge:
1. Demand analysis and price optimization
Data science is transforming parallel trade mitigation through advanced analytics and constraint modeling. This allows you to implement pricing strategies to minimize revenue leakage and optimize profitability across regions.
The approach involves:
Demand Segmentation Manufacturers leverage critical parameters to forecast cross-border demand:
- Baseline demand
- Price elasticity
- Regulatory price limits
Demand Breakdown
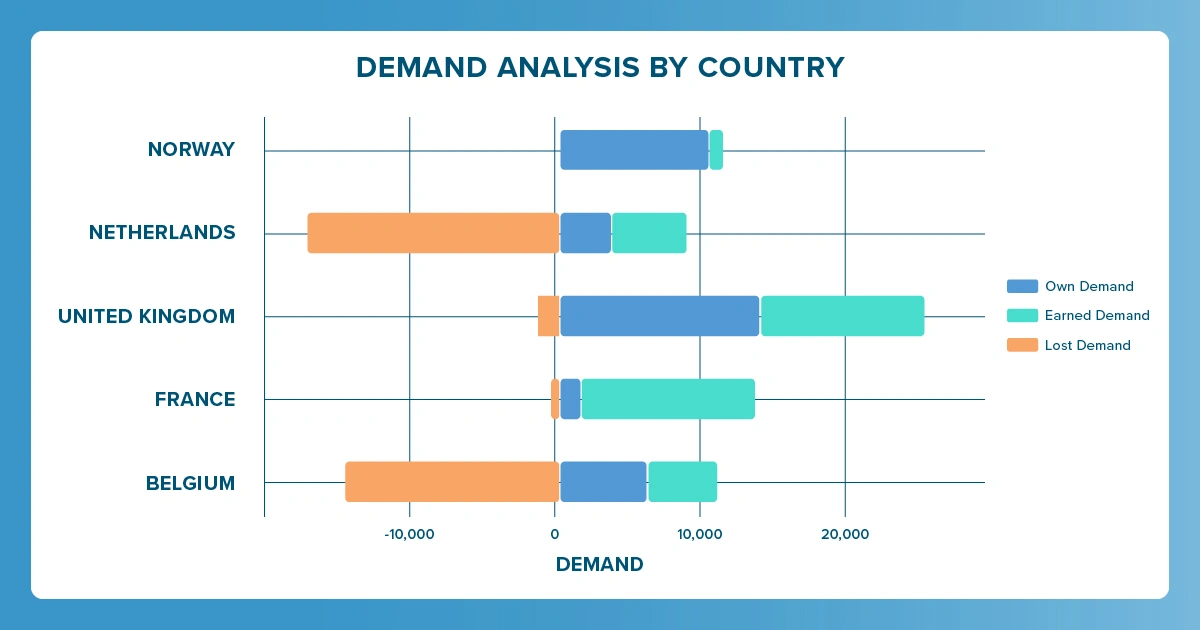
- Own Demand: Portion of product volume retained locally, not leaving the country
- Earned Demand: Volume imported from other countries through parallel trade
- Lost Demand: Volume exported or lost due to price elasticity effects
By applying demand analytics, you can visualize trade flow dynamics and assess the impact on demand for each country. Let’s look at an example:
When examining the demand analysis chart, key insights emerge:
- A country with significant "lost demand" indicates product exports, potentially creating local shortages
- A country with high "earned demand" benefits from imported sales via parallel trade
These insights enable you to explore strategic scenarios:
First, calculate total profit under current prices, considering parallel trading flows. Then, conduct a joint price optimization that:
- Selects prices for each country
- Simultaneously updates demand flows
- Tracks parallel trade movements
By testing assumptions like corridor restrictions or shipping costs, you can identify a global pricing strategy that:
- Maximizes overall profit
- Minimizes revenue leakage
Ultimately, this method helps you determine an optimal pricing strategy that reduces profit erosion while complying with market rules. You'll gain insights into how trade flows and pricing decisions impact your global profit, revenue and margins.
2. Conditional pricing for wholesalers
This strategy discourages parallel trade through conditional pricing structures:
- Adjusting Wholesale Prices: Manufacturers sell products at higher wholesale prices to distributors suspected of engaging in parallel trade.
- Credit price differences only after sell proof: Distributors can claim rebates or credits to encourage compliance by providing proof that the products were sold within the intended country.
These approaches disincentivize parallel trade while maintaining accessibility in priority, lower-priced markets. Automating this process through sophisticated software solutions, leveraging data analytics and intelligent pricing strategies, minimizes manual work and errors, ensuring seamless execution.
Don’t wave goodbye to your claim of profits! Watch this on-demand webinar
Get the latest news, updates, and exclusive insights from Vistex delivered straight to your inbox. Don’t miss out—opt in now and be the first to know!